All the Math You Need to Know for 6th Grade
The mathematical vocabulary terms below can exist found in the Mathworks Math Explorations textbooks.
A B C D E F G H I J M L M Due north O P Q R Southward T U V W 10 Y Z
Absolute Value
- The accented value of a number is its distance from nil.
- For any 10, |ten| is defined every bit follows: | x |= 10, if x > 0, and | ten |= −x, if 10 < 0
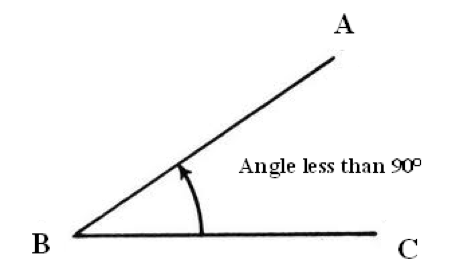
Acute Angle
An angle whose measure is greater than 0 degrees and less than 90 degrees.
Acute Triangle
A triangle in which all iii angles are acute angles.
Improver Property of Equality
If a = b, so a + c = b + c. This property states that adding the aforementioned amount to both members of an equation preserves the equality.
Additive identity
A property that states that for any number 10, x + 0 = x, null is the additive identity.
Additive Inverse
For whatsoever number x, there exists a number −10, such that x + −x= 0. This means that there exists a pair of numbers (like 5 and –5) that are the same distance from nothing on the number line, and when added together will always produce a sum of zero. These pairs of numbers are as well sometimes called "opposites."
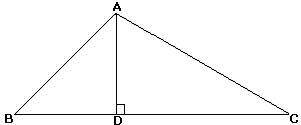
Altitude of a Triangle
A segment fatigued from a vertex of the triangle perpendicular to the reverse side of the triangle, chosen the base (or perpendicular to an extension of the base of operations).
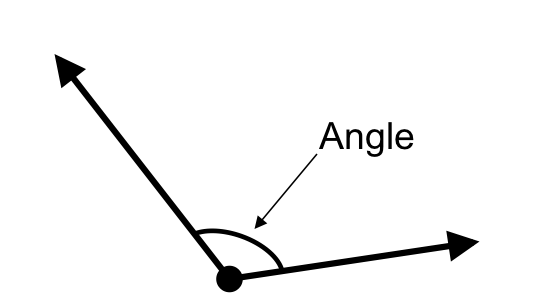
Angle
An angle is formed when two rays share a common vertex.
Surface area Model
A mathematical model based on the expanse of a rectangle, used to stand for multiplication or partial parts of a whole.
Associative Holding of Addition
For any numbers x, y , and z: (x + y) + z = x + (y + z). The associative holding of addition states that the order in which you group variables or numbers does not affair in determining the final sum.
Associative Property of Multiplication
For any numbers x, y , and z: (xy) z = x (yz). The associative property of multiplication states that the order in which you group variables or numbers does not affair in determining the concluding production.
Attribute
A distinguishing characteristic of an object. For instance, two attributes of a triangle are angles and sides.
Axis
A number line in a plane. Plural form is axes. Also run into: Coordinate Plane.
Bar Graph
A graph in which rectangular bars, either vertical or horizontal, are used to display data.
Base
- If any number ten is raised to the nth ability, written as ten^northward, x is called the base of the expression;
- Any side of a triangle;
- Either of the parallel sides of a trapezoid;
- Either of the parallel sides of a parallelogram.
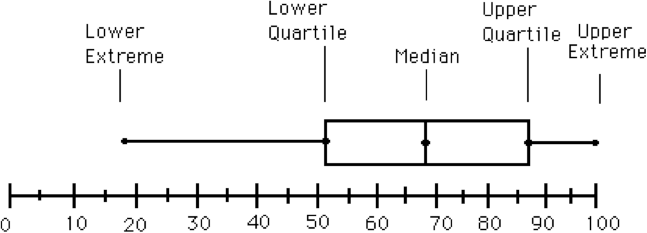
Box and Whisker Plot
For information ordered smallest to largest the median, lower quartile and upper quartile are found and displayed in a box along a number line. Whiskers are added to the correct and left and extended to the least and greatest values of the data.
Cartesian Coordinate System
Run across: Coordinate Plane
Center of a Circle
A bespeak in the interior of the circle that is equidistant from all points of the circle.

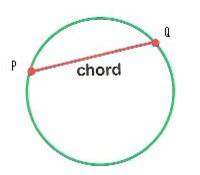
Chord
A segment whose endpoints are points of a circle.
Circle
The set of points in a plane equidistant from a point in the plane.
Circumference
The distance effectually a circle. Its length is the product of the diameter of the circle and pi.
Coefficient
In the product of a constant and a variable the abiding is the numerical coefficient of the variable and is frequently referred to simply every bit the coefficient.
Common Denominator
A common multiple of the denominators of two or more fractions. Also run into: Least Common Denominator
Common Cistron
A gene that two or more integers have in mutual. Also run across: Greatest Mutual Factor.
Common Multiple
See: Least Common Multiple.
Complement
The complement of a set E is a set of all the elements that are not in E.
Complementary Angles
Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures totals ninety degrees.
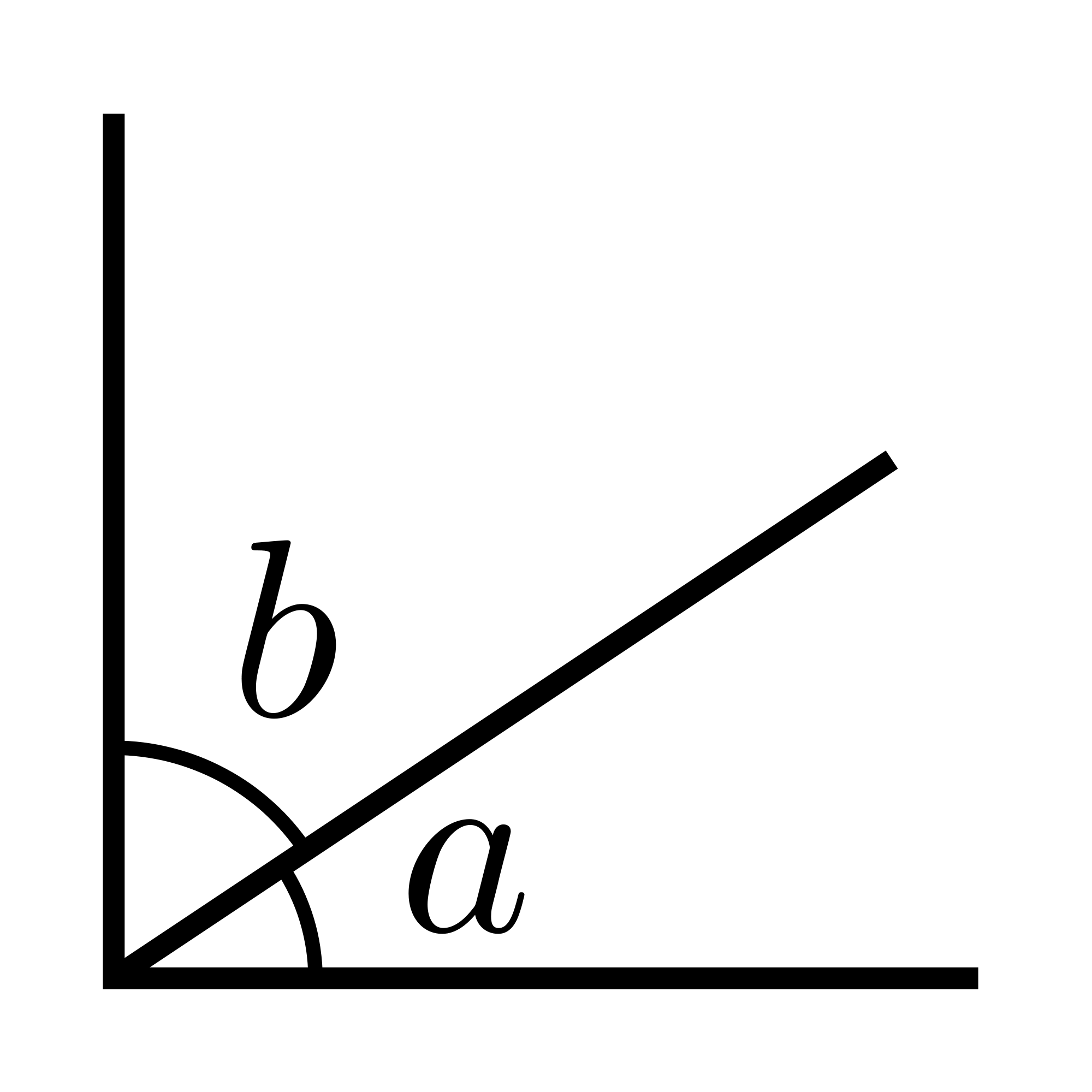
Composite Number
A prime number number is an integer p greater than 1 with exactly two positive factors: i and p. A composite number is an integer greater than i that has more than 2 positive factors. The number 1 is the multiplicative identity; that is, for any number n, northward · 1 = n. The number 1 is neither a prime number nor a blended number.
Chemical compound Event
A subset of a sample space containing two or more outcomes.
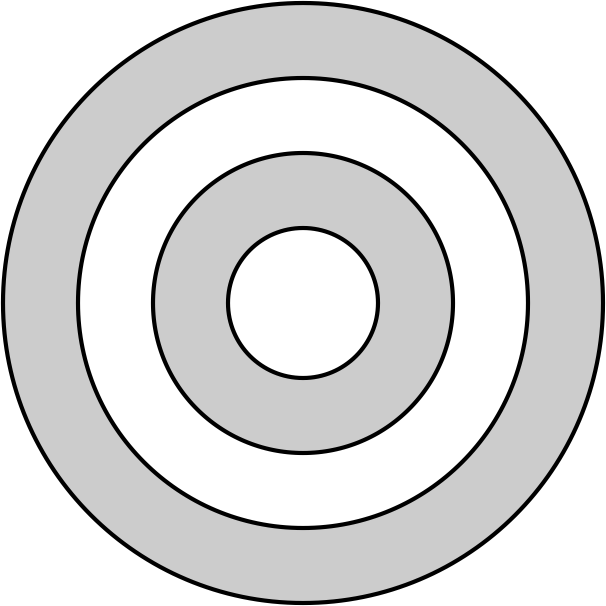
Concentric circles
Circles with the same center and in the same airplane that have different radii.
Cone
A three-dimensional figure with a circular base of operations joined to a point called the noon.

Congruent
Used to refer to angles or sides having the same measure and to polygons that have the aforementioned shape and size.
Theorize
An assumption that is thought to be truthful based on observations.
Constant
A fixed value.
Coordinate(s)
A number assigned to each bespeak on the number line which shows its position or location on the line. In a coordinate airplane the ordered pair, (10,y), assigned to each indicate of the plane, shows the indicate's position in relation to the x-axis and y-axis.
Coordinate Plane
A aeroplane that consists of a horizontal and vertical number line, intersecting at correct angles at their origins. The number lines, called axes, divide the plane into four quadrants. The quadrants are numbered I, II, III, and Iv beginning in the upper correct quadrant and moving counterclockwise.

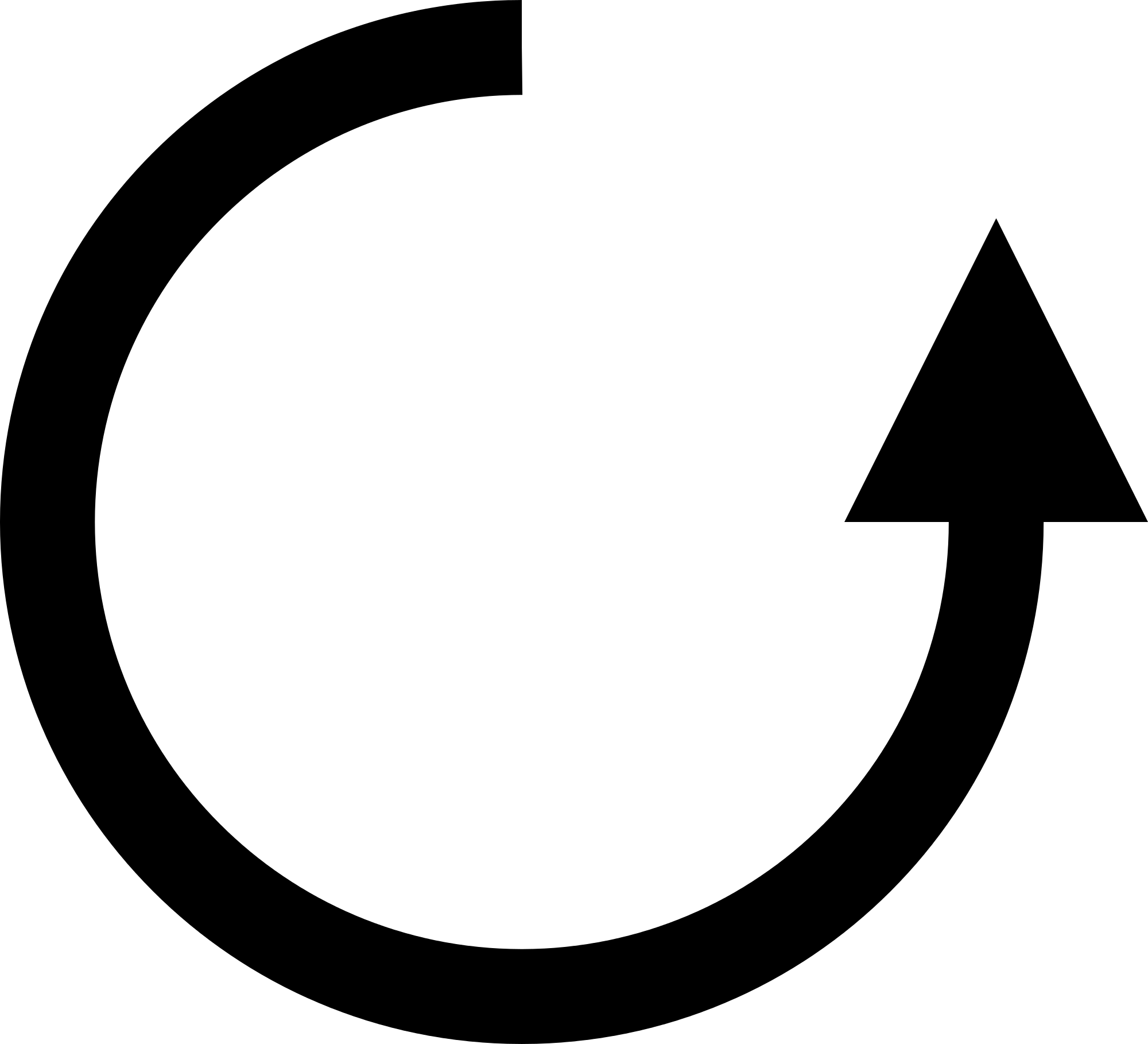
Counterclockwise
A circular movement opposite to the direction of the movement of the hands of a clock.
Counting Numbers
The counting numbers are the numbers in the following never-catastrophe sequence: 1, 2, three, 4, five, vi, 7... We can besides write this as +ane, +2, +iii, +four, +5, +vi, +vii,... These numbers are besides called the positive integers or natural numbers.
Cube
- A three-dimensional shape having half-dozen congruent square faces.
- The tertiary ability of a number.
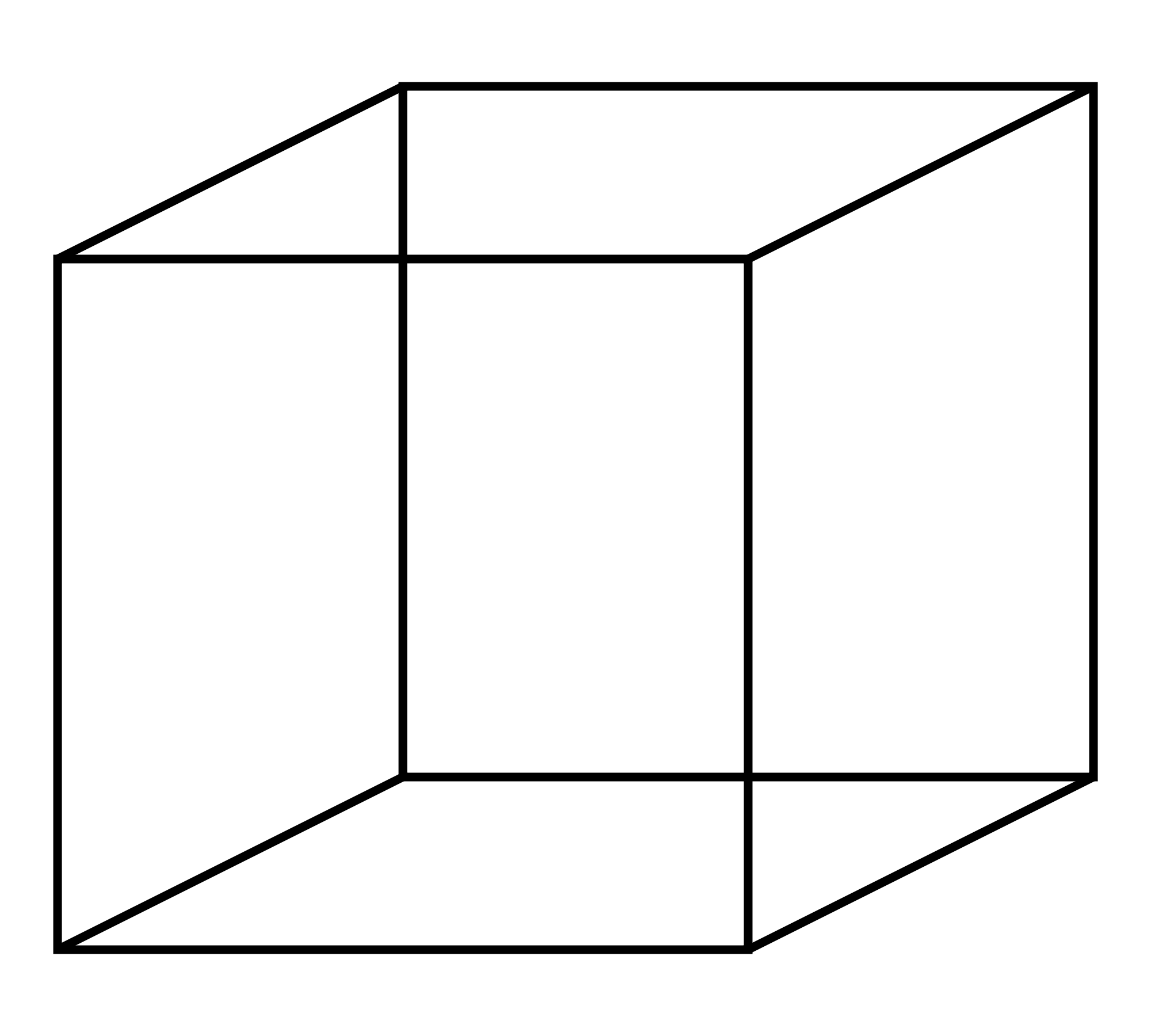
Cylinder
A iii-dimensional figure with parallel circular bases of equal size joined by a lateral surface whose cyberspace is a rectangle.

Information
A collection of information, frequently in the form of numbers.
Data Analysis
The process of making sense of collected data.
Information Point
Each individual piece of information collected in a set of data.
Degree
- The circumference of a circle is divided into 360 equal parts or arcs. Radii drawnto both ends of the arc form an angle of one degree.
- The degree of a term is the sum of the exponents of the variables.
- A degree is also unit of measurement of measurement used for measuring temperature.
Denominator
The denominator of a fraction indicates into how many equal parts the whole is divided. The denominator appears beneath the fraction bar.
Diameter
A segment with endpoints on the circle that passes through its center.
Dividend
The quantity that is to be divided.
Divisibility
Suppose that n and d are integers, and that d is not 0. The number n is divisible past d if there is an integer q such that n = dq. Equivalently, d is a factor of due north or north is a multiple of d.
Division Algorithm
Given two positive integers a and b, we can always find unique integers q and r such that a= bq + r and 0≤ r < b. Nosotros call a the dividend, b the divisor, q the caliber, and r the residue.
Divisor
The quantity by which the dividend is divided.
Domain
The set of input values in a function.
Edge
A segment that joins sequent vertices of a polygon or a polyhedron.
Elements
Members of a gear up.
Empirical Probability
Probability determined by real information collected from real experiments.
Equation
A math sentence using the equal sign to state that 2 expressions represent the aforementioned number.
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle with three congruent sides. An equilateral triangle also has iii coinciding angles, which we can likewise call equiangular triangle.
Equivalent
- A term used to describe fractions or ratios that are equal.
- A term used to describe fractions, decimals, and percents that are equal.
Event
An result is any subset of the sample space. A elementary event is a subset of the sample space containing only i possible result of an experiment. A compound event is a subset of the sample space containing 2 or more outcomes.
Experiment
A repeatable action with a set of outcomes.
Exponent
Suppose that n is a whole number. Then, for any number x, the nth power of x, or x to the nth power, is the product of north factors of the number x. This number is normally written x^n. The number x is usually called the base of the expression ten^n, and northward is chosen the exponent.
Exponential Notation
A notation that expresses a number in terms of a base of operations and an exponent.
Expression
A mathematical phrase like "yard + i" used to describe quantities mathematically with numbers and variables.
Confront
Each of the surface polygons that form a polyhedron.
Gene
An integer that divides evenly into a dividend. Utilize interchangeably with divisor except in the Division Algorithm.
Factorial
The factorial of a non-negative number n is written northward! and is the production of all positive integers less than or equal to n. By definition 0!= i!= i.
Fraction
Numbers of the course m/n, where n is not zero.
Frequency
The number of times a data betoken appears in a data set.
Function
A function is a dominion that assigns to each member of a prepare of inputs, called the domain, a member of a set of outputs, called the range.
Graph of a Office
The pictorial representation of a function.
Greater than, Less Than
Suppose that ten and y are integers. We say that ten is less than y, x < y, if 10 is to the left of y on the number line. Nosotros say that 10 is greater than y, x > y, if 10 is to the correct of y on the number line.
Greatest Common Gene, GCF
Suppose m and north are positive integers. An integer d is a common factor of m and n if d is a factor of both m and north. The greatest common cistron, or GCF, of grand and n is the greatest positive integer that is a gene of both thousand and due north. We write the GCF of m and n every bit GCF (m,due north).
Superlative
The length of the perpendicular between the bases of a parallelogram or trapezoid; also the distance of a triangle.
Horizontal Axis
See: Coordinate Aeroplane.
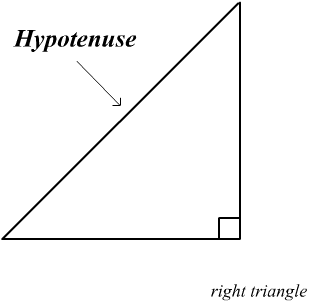
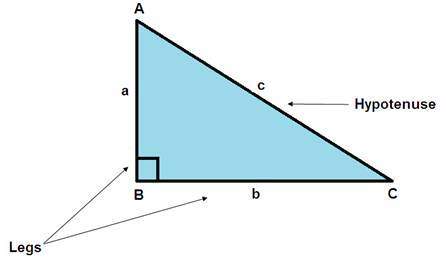
Hypotenuse
The side reverse the right angle in a right triangle.
Improper Fraction
A fraction in which the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
Contained Events
If the upshot of an event does not affect the outcome of other events.
Input Values
The values of the domain of a function.
Integers
The collection of integers is equanimous of the counting numbers, the negatives, and nothing; ... −4, −three, −2, −1, 0, i, two, 3, 4...
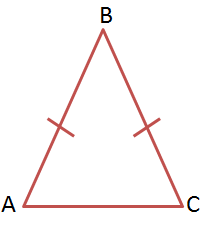
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle with at least two sides of equal length.
Lateral Area
The surface area of any three-dimensional figure excluding the area of whatever surface designated as a base of the figure.
Lattice Bespeak
A point of the coordinate plane, (x,y), in which both x and y are integers.
Least Mutual Denominator
The to the lowest degree common denominator of the fractions p/northward and k/1000 is the to the lowest degree common multiple of n and one thousand, LCM(n, m).
Least Common Multiple, LCM
The integers a and b are positive. An integer m is a common multiple of a and b if m is a multiple of both a and b. The least common multiple, or LCM, of a and b is the smallest integer that is a mutual multiple of a and b. Nosotros write the LCM of a and b as LCM (a,b).
Legs
- The 2 sides of a right triangle that form the right angle.
- The equal sides of an isosceles triangle or the not-parallel sides of a trapezoid.
Less than
Meet: Greater Than.
Line graph
A graph used to brandish information that occurs in a sequence. Consecutive points are continued by segments.
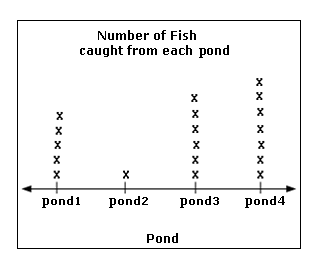
Line Plot
A graph that shows frequency of data along a number line.
Linear Model for Multiplication
Skip counting on a number line.
Mean
The average of a set of information; sum of the data divided by the number of items. Also called the arithmetic mean or average.
Measures of Cardinal Tendency
Generally measured by the mean, median, or manner of the information set.
Median
The heart value of a prepare of data arranged in increasing or decreasing order. If the prepare has an fifty-fifty number of items the median is the average of the eye two items.
Missing Factor Model
A model for division in which the quotient of an indicated division is viewed as a missing gene of a related multiplication.
Mixed fraction (Numbers)
The sum of an integer and a proper fraction.
Mode
The value of the element that appears most oftentimes in a data gear up.
Multiplicative Identity
See: Composite Numbers.
Multiplicative Inverse
The number x is called the multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of north, n ≠ 0, if x · north = 1.
Natural Numbers
See: Counting Numbers.
Negative Integers
Integers less than aught.
Notation
A technical organisation of symbols used to convey mathematical information.
Number Line
A pictorial representation of numbers on a straight line.
Numerator
The expression written above the fraction bar in a common fraction to indicate the number of parts counted.
Obtuse Bending
An angle whose measure is greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees.
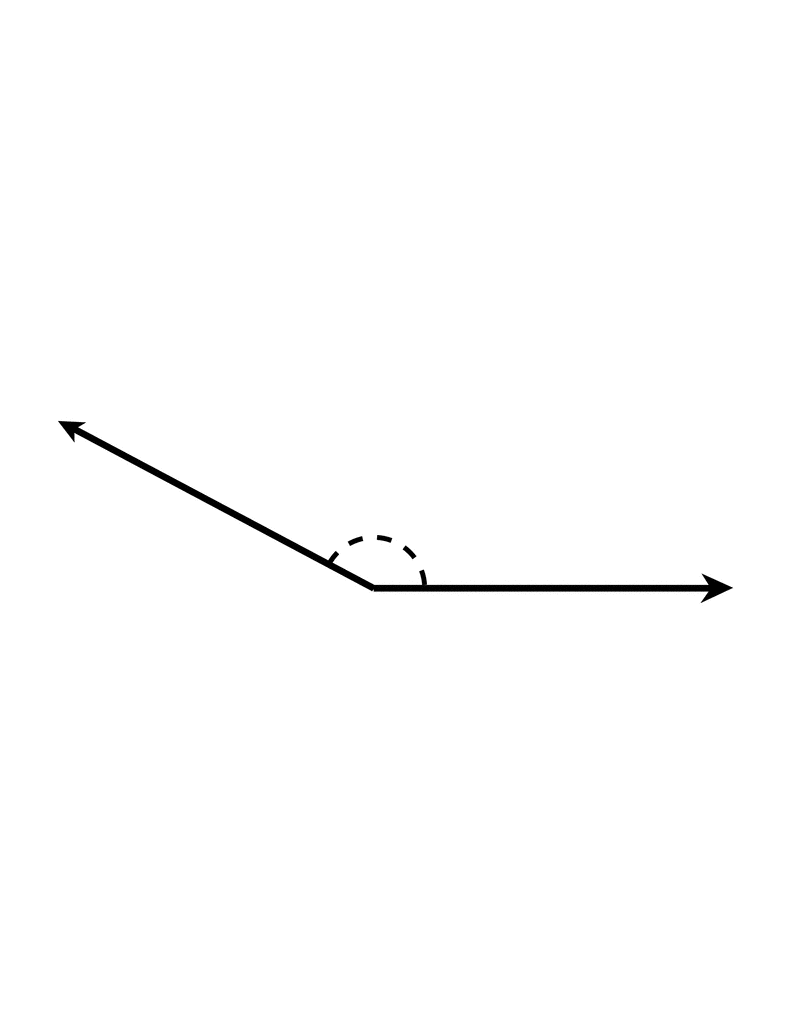
Obtuse Triangle
A triangle that has one birdbrained angle.
Order Of Operations
The order of mathematical operations, with computations inside parentheses to be done start, and addition and subtraction from left to correct done last.
Ordered Pair
A pair of numbers that represent the coordinates of a point in the coordinate aeroplane with the first number measured along the horizontal scale and the second along the vertical scale.
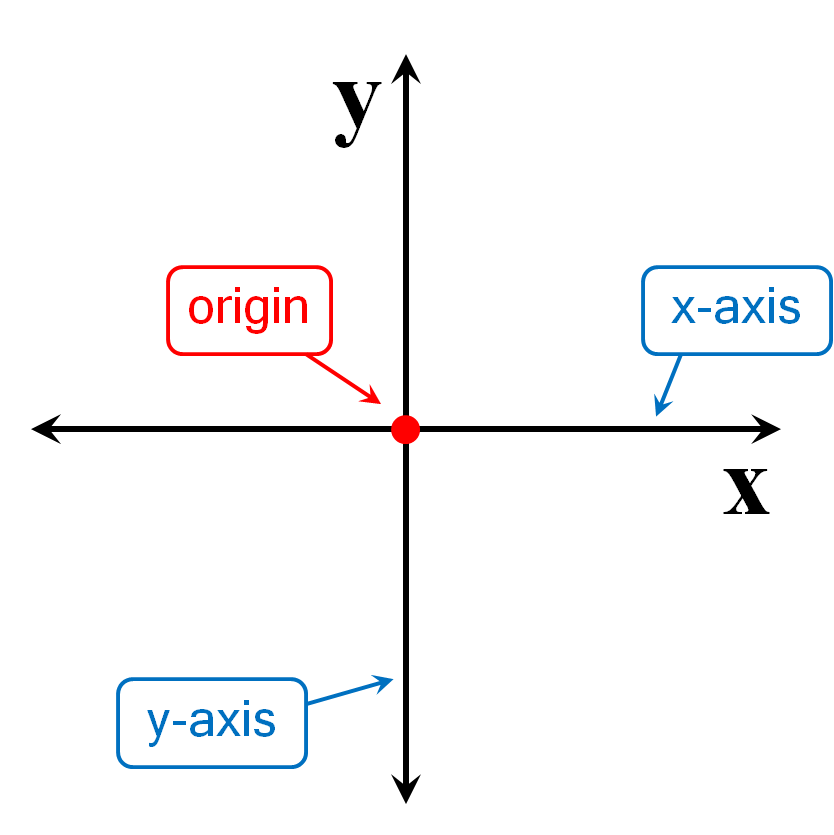
Origin
The signal with coordinate 0 on a number line; the point with coordinates (0,0) in the coordinate aeroplane.
Outcomes
The set of possible results of an experiment.
Outlier
A term referring to a value that is drastically dissimilar from most of the other data values.
Output Values
The set of results obtained past applying a function dominion to a ready of input values.
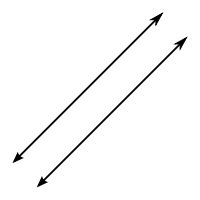
Parallel Lines
Ii lines in a aeroplane that never intersect.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a iv-sided effigy with reverse sides parallel.

Percentage
A manner of expressing a number as parts out of 100; the numerator of a ratio with a denominator of 100.
Perfect Cube
An integer north that can be written in the form n= k³, where k is an integer.
Perfect Square
An integer n that can be written in the form n= one thousand², where k is an integer.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides.
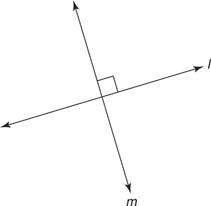
Perpendicular
Two lines or segments are perpendicular if they intersect to class a right angle.
Pi
The ratio of the circumference to the diameter of whatsoever circle, represented either by the symbol π, or the approximation 22/7 , or 3.1415926...
Pie (Circumvolve) Graph
A graph using sectors of a circumvolve that are proportional to the percent of the data represented.
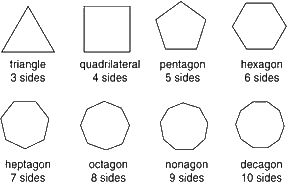
Polygon
A elementary, closed, plane effigy formed by three or more line segments.
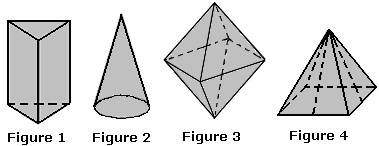
Polyhedron
A three-dimensional effigy with four or more faces, all of which are polygons.
Positive Integers
See: Counting Numbers.
Power
See: Exponent.
Prime
See: Blended Number.
Prime Factorization
The process of finding the prime factors of an integer. The term is likewise used to refer to the result of the process.
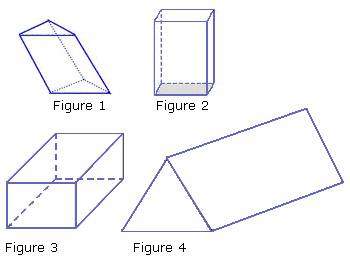
Prism
A blazon of polyhedron that has 2 bases that are both congruent and parallel, and lateral faces which are parallelograms.
Probability
In an experiment in which each effect is equally likely, the probability P(A) of an event A is 1000/due north where g is the number of outcomes in the subset A and n is the total number of outcomes in the sample infinite S.
Proper Fraction
A fraction whose value is greater than 0 and less than one.
Proportion
An equation of ratios in the form a/b = c/d, where b and d are not equal to zero.
Protractor
An musical instrument used to measure angles in degrees.
Quadrant
See: Coordinate Airplane.
Quadrilateral
A aeroplane figure with four straight edges and iv angles.
Quotient
The result obtained by doing sectionalization. See the Division Algorithm for a different utilise of quotient.
Radius
The distance from the heart of a circle to a point on the circle. Plural class is radii.
Range
The divergence between the largest and smallest values of a data set. See Role for another meaning of range.
Rate
A rate is a partitioning comparing betwixt two quantities with dissimilar units. As well see Unit of measurement Rate.
Ratio
A sectionalization comparison of two quantities with or without the same units. If the units are dissimilar they must be expressed to brand the ratio meaningful.
Rational Number
A number that can be written every bit a/b where a is an integer and b is a natural number.
Ray
Part of a line that has a starting betoken and continues forever in only one management.
Reciprocal
Run across: Multiplicative Inverse.
Regular Polygon
A polygon with equal side lengths and equal bending measures.
Relatively Prime number
Two integers k and n are relatively prime number if the GCF of m and n is 1.
Rest
See: Division Algorithm.
Repeating Decimal
A decimal in which a cycle of i or more digits is repeated infinitely.
Right Angle
An angle formed by the intersection of perpendicular lines; an angle whose measure is 90º.
Right Triangle
A triangle that contains a correct angle.
Sample Space
The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
Scaffolding
A method of division in which partial quotients are computed, stacked, and then combined.
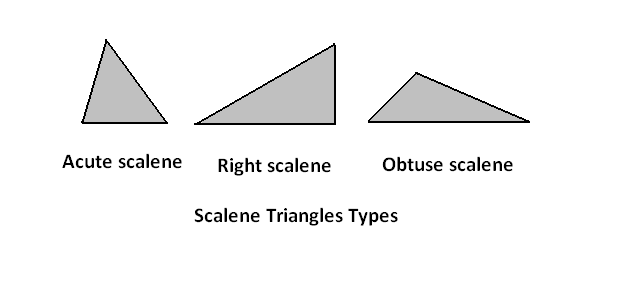
Scalene Triangle
A triangle with all iii sides of different lengths is called a scalene triangle.
Scaling
- A process by which a shape is reduced or expanded proportionally.
- Choosing the unit of measure to exist used on a number line.
Sector
A office of a circumvolve that represents the interior portion of the circumvolve between two radii.
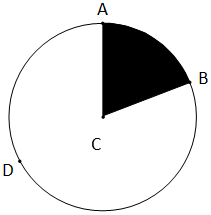
Sequence
A list of terms ordered by the natural numbers.
Set
A collection of objects or elements.
Simple Issue
Meet: Result
Simplest Form of a Fraction
A form of a fraction in which the greatest mutual cistron of the numerator and denominator is one.
Simplifying
The process of finding equivalent fractions to obtain the simplest form.
Skewed
An uneven representation of a set of data.
Slant Height
An altitude of a face of a pyramid or a cone.
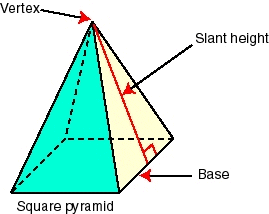
Square Root
For not-negative numbers x and y, y= x , read "y is equal to the square root of x," means y²= 10.
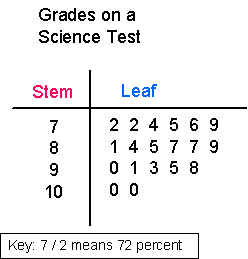
Stalk and Leaf Plot
A method of showing the frequency of a sure information by sorting and ordering the values.
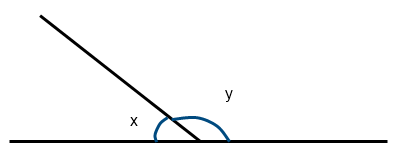
Directly Angle
An angle with a measure out of 180 degrees formed by reverse rays.
Subset
Set B is a subset of set A if every element of set B is also an element of set A.
Supplementary
2 angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures totals 180º.
Surface Area
The surface surface area of a three-dimensional figure is the area needed to form its outside.
Terminating Decimal
If the quotient of a segmentation problem contains a remainder of cipher, the quotient is said to exist a terminating decimal.
Tessellation
Tiling of a plane with one or more shapes every bit a way of roofing the aeroplane with the shape(southward) with no gaps or overlaps.
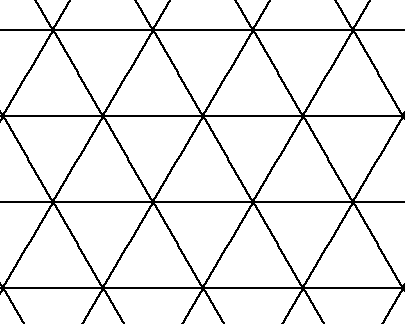
Theoretical Probability
Probability based on thought experiments rather than a collection of information.
Translation
A transformation that slides a figure a certain distance along a line in a specified direction.
Trapezoid
A four sided plane figure with exactly one set of parallel sides.
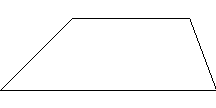
Tree Diagram
- A process used to observe the prime factors of an integer.
- A method to organize the sample space of compound events.
Triangle
A airplane figure with three directly edges and three angles.
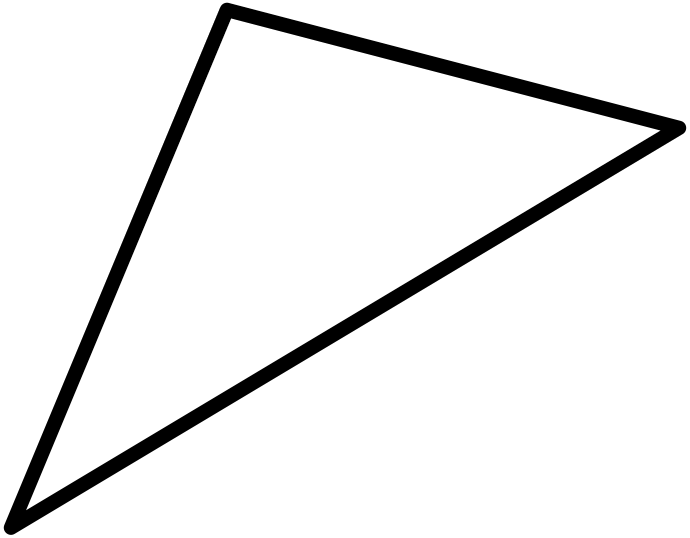
Trichotomy
A property stating that exactly one of these statements is true for each real number: it is positive, negative, or cypher.
Unit Fraction
For an integer northward, the multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of n is the unit fraction 1/n. ane/n is said to be a unit fraction considering its numerator is 1.
Unit Rate
A ratio of ii unlike quantities that has a denominator of 1 unit.
Variable
A letter or symbol that represents an unknown quantity.
Venn Diagram
A diagram involving ii or more overlapping circles that aids in organizing data.
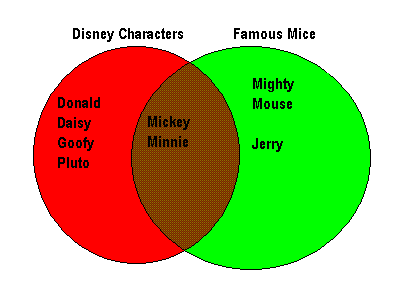
Vertex
- The common endpoint of two rays forming an angle.
- A indicate of a polygon or polyhedron where edges meet.
Vertical Angles
A pair of angles of equal mensurate less than 180° that are formed by opposite rays of a pair of intersecting lines.
Vertical Centrality
See: Coordinate Plane.
Book
A measure of space; the number of unit cubes needed to fill a iii-dimensional shape.
Whole Numbers
The whole numbers are the numbers in the following never-catastrophe sequence: 0, 1, two, 3, four, 5, .... These numbers are also called the non-negative integers.
x-axis
The horizontal axis of a coordinate plane.
y-centrality
The vertical centrality of a coordinate plane.
x-coordinate
The first number provided in an ordered pair (a, b).
y-coordinate
The 2nd number provided in an ordered pair (a, b).
Source: https://www.txstate.edu/mathworks/ME-Curriculum/math-explorations-for-teachers/online-learning-tools/illustrated-math-glossary/6th-grade-math-vocabulary.html
0 Response to "All the Math You Need to Know for 6th Grade"
Post a Comment